The outside of the ear drum is exposed to water pressure when diving. The space on the inside of the eardrum should be equalized by the pressurized air. This is facilitated by the air coming in through the Eustachian tube (see arrow) one end of which is connected to the middle ear and the other end to the back of the throat. This end is usually closed but can be opened by jaw movement and the action of “clearing.” As the diver moves deeper the increasing pressure must be equalized to avoid pain or even damage to the eardrum.
The muscle that assists in the opening of the Eustachian tube is called the Tensor Velli Palatini and it develops from the same tissues and shares nerve connections with the chewing muscles. Because of this early developmental connection these muscles can at times act together (we call this synchrony). When this happens and the divers jaw muscles are tense the TVP muscle will not easily allow the air to enter the Eustachian tube. The diver now has a significant problem clearing.
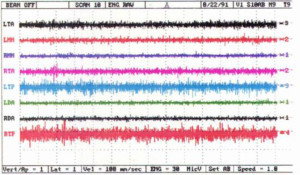
SeaCure has been documented by electromyographic muscle testing to reduce muscle activity by up to 90% over conventional mouthpieces (see graph below). Because the mouthpiece grips the diver, the diver does not have to grip the mouthpiece. SeaCure has also been specifically designed to provide maximum stiffness (unlike some moldable mouthpieces) which again reduces muscle activity. This reduction of muscle activity can help divers who are prone to clearing problems. Many divers have told us of this very important benefit.
Standard Mouthpiece Muscle Activity
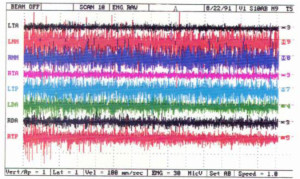
SeaCure Mouthpiece Muscle Activity